Equality of Integer and Long objects in Java
TLDR
Use the equals method when checking if Integer or Long objects are equal.
Integer a = 1000;
Integer b = 1000;
a.equals(b); // true
a == b; // false
Using == sometimes returns incorrect results
Checking the equality of Integer objects with the == operator sometimes returns incorrect results. This also happens with Long objects.
Integer a = 1000;
Integer b = 1000;
a.equals(b); // true
a == b; // false
The Integers a and b are equal but using the == operator returns false. The confusing part is that this is not always true, as you can see in the below example.
Integer a = 100;
Integer b = 100;
a.equals(b); // true
a == b; // true
This does not happen when at least one of the sides is primitive ints.
Integer == intint == int
I found out that == returns a correct result from -128 to 127. You can see this in the code below.
Integer a = 127;
Integer b = 127;
a == b; // true
a = 128;
b = 128;
a == b; // false
a = -128;
b = -128;
a == b; // true
a = -129;
b = -129;
a == b; // false
I haven't really looked into why this is, but I have found the numbers -128 and 127 in the Integer class. I am guessing that the IntegerCache class has got to do with this.
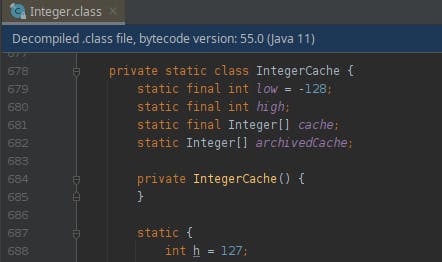
I decided to stick with using Integer objects and using the equals method when checking for equality. Because I didn't want to worry about accidentally checking two Integer objects with ==.
Thanks!
Thank you for reading till the end!
I would be happy to see some feedback, so please let me know your thoughts!
